Hard Water Softener & Filtration
Water softeners for hard water, iron, manganese, arsenic, ph adjustment & sediment
Our state-of-the-art water softening, filtration and conditioning systems are designed to provide crystal clear and safe water throughout your home. Call us for a free in- home consultation, basic on site testing and a speedy Ma Certified Lab Analysis. All systems are designed by Certified Water Specialists based on your individual test results.
 Water Softening
Water Softening- Water Hardness and Scale Control
- PH Neutralizing
- Iron & Manganese Removal
- Arsenic Removal
- Nitrates Removal
- Sediment Removal
- Radon in Water Removal
Important Information from ThinkPureWater
on Solving Your Home Water Problems.
Soft and Hard Water
Nature, through the hydrological cycle and natural distillation, is constantly softening our waters. All rainfall is mineral free soft water. Throughout time, all living things on Earth drink or absorb surface waters that fell as rain. All rainwater filling streams, rivers and lakes starts out as mineral free water. Natural mineral springs, where waters emerge from the Earth, filled with hardness minerals, are rare and are the exception. Where water is scarce, humans dig wells and hard, mineralized hard water is brought to the surface for use.
 WELL WATER ISSUES & TESTING
WELL WATER ISSUES & TESTING
Although the prevailing thought is that well water is safe to drink and good for you, wells right here in MA can have high levels of Hardness Minerals as well as Arsenic, Radon, Radium, Uranium, Nitrates & Bacteria etc. Besides these naturally occurring toxic substances, wells can become polluted with industrial chemicals. Families owning a well or considering buying a property with a well, should have a MA State Certified Lab test done and have a document describing everything about the water’s condition. This is especially true if you are drinking the water. Choosing the right test and not going overboard is important. We can advise you on the right test and get it off to the lab promptly.
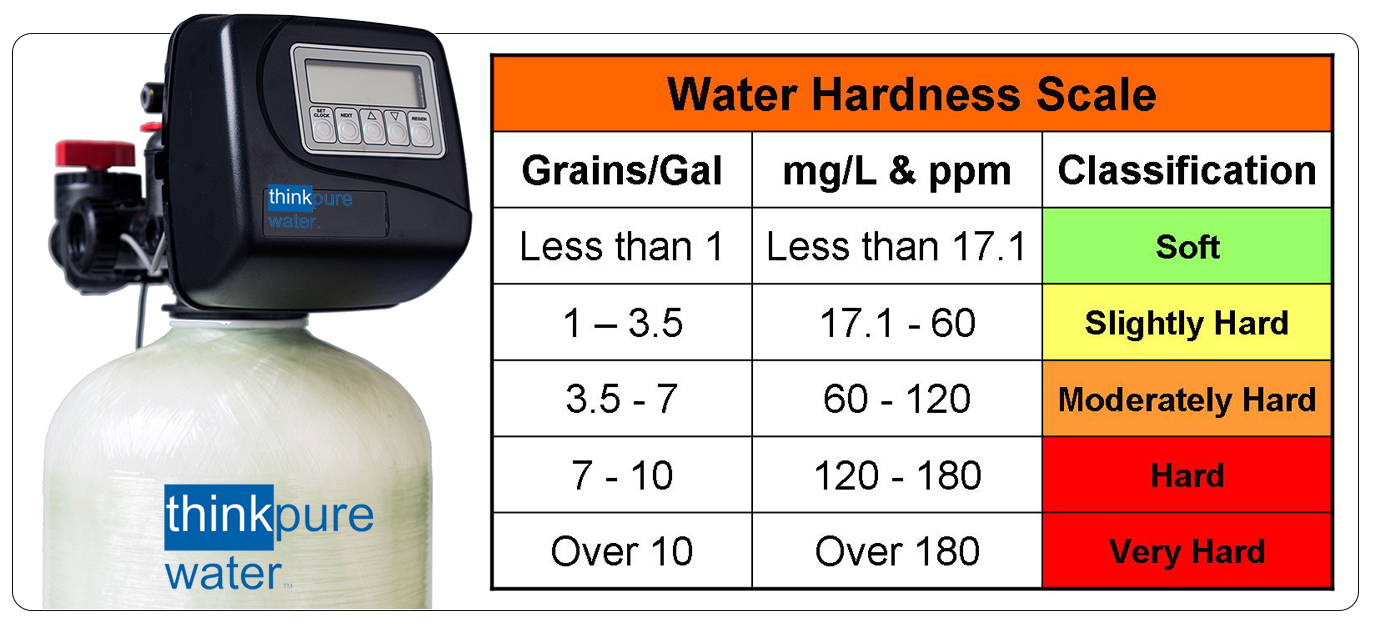
WHAT IS HARD WATER?
Hard water is defined as any water having over 3.5 Grains Per Gallon ( GPG ) of dissolved Calcium and Magnesium. Hardness is also measured in Mg/l ( milligrams per liter ) and PPM ( parts per million ). Mg/l and PPM are equal and the same. GPG is calculated by dividing Mg/l or PPM x 17.1. Do not depend on a TDS Meter ( Total Dissolved Solids ) to provide hardness levels as they measure the electrical conductivity of all dissolved substances, such as components of salt, not just hardness minerals.
Call us for a free appointment to evaluate your water issues, and recommend the correct equipment to remedy the problem. Water test kits are on our trucks or can be mailed to your home without delay. Call 508.272.6636
WATER SOURCES
The majority of water softeners are installed to correct hardness and iron issues with private or semi private well water. Some town water systems are sourced from wells or groups of wells combined with surface water like those of Wayland, Sudbury. Dedham, Natick and Needham, etc. which all have hard water. Certain towns can have hard and soft water, depending on where you live. Towns using only MWRA water, sourced from places like Quabbin Reservoir enjoy naturally soft water with an average of just 1 GPG or around 17 PPM of hardness.
EFFECTS OF HARD WATER
Hard water scale can build up rock hard crusty deposits on plumbing fixtures. It can run from whitish to brownish orange where iron is also present. It can etch your shower glass, clog up your shower head and eat away the polished surfaces of marble, granite and porcelain. Soleniods in any water using appliance like dishwashers can clog with scale, leak or fail to work. Dishes and glasses can be impossible to rinse really well. It can build up inside pipes and completely encrust heating elements, dramatically lowering their efficiency and cause increased energy bills. Along with low ph, it can eat thru your copper pipes as well as clog them and restrict water flow. It can also be difficult to lather up with hard water. Less soap and detergent is needed when water is naturally soft or softened. Hard water is generally not considered unhealthy to drink but anything can be harmful in excess.
WATER SOFTENER THEORY & REGENERATION PROCESS
Water softeners work by passing the raw hard water thru a tank containing millions of resin beads. The beads are a little larger than a grain of sand and are negatively charged. Calcium and Magnesium ions are positively charged and build up on the resin beads leaving the water softened. Water Softeners work amazingly well, as a very exact science is at work. After a certain amount of time and water usage, the resin will no longer attract the hardness minerals as they are fully coated. They now must be rinsed clean or regenerated to work again. All water softeners have a resin tank with a control head and a salt brine tank. The salt tank starts out with about three to four 40 lb bags. 3 to 4 gallons of water is manually added to begin the process. From there on, the control automatically replaces the water in the brine tank so the brine is always ready for the next cycle.
Call us for a free appointment to evaluate your water issues, and recommend the correct equipment to remedy the problem. Water test kits are on our trucks or can be mailed to your home without delay. Call 508.272.6636
REGENERATION FREQUENCY & SALT USAGE
Re-generation frequency varies according to water usage, hardness level and cubic feet or size of resin tank. Usually its once every two weeks and set to take place at 2:00 am. Modern, electronic metered use, control heads will regenerate only when the calculated amount of water is used, thus preventing regeneration before it is actually needed. If you are away and not using water, the regen will not occur. These units reduce salt and water usage. One caveat is that if your iron level is above a certain threshold, regen must occur every 2 weeks whether you use water or not. Higher levels of iron in water cannot be allowed to sit in the resin bed or it will become iron fouled and stop working. Average regens use about 8 to 12 lbs of salt. The regeneration process uses salt brine to clear the resin beads of hardness minerals an can take from one to two hours depending on various parameters.
THE REGENERATION CYCLE
The regen cycle is carefully calculated based on cubic ft of softener, water hardness, alkilinity and iron levels. When this data is entered into a computer in the control head it will automatically read out the number of gallons that can be softened between each regen. If 2000 gallons is calculated, the control head will count each gallon that passes thru the system and initiate a regen at 2:00 am on the nearest night before the 2000 gallons is used. Now the softener is ready to soften the water for another cycle.
BRINE DISCHARGE
The discharge from the rinse must be correctly disposed of. In Massachusetts, it cannot be discharged into a septic system. Elevated levels of salt can interfere with natural bacteria levels and prevent proper septic function. It can be sent into a drywell outside the home or, in the case of town sewer, into the drain. A P-Trap, similar to a washing machine drain pipe is acceptable according to the plumbing code. If none exists, one can be cut into the main drain in the basement. It is important to pull a permit and have the local inspector sign off on the install.
pH NEUTRALIZER
In some cases, where the PH is lower than 6.8, a pH Neutralizer tank must be installed ahead of the softener. This is designed to raise the pH of the finished water to prevent it from becoming too corrosive and stripping copper from water pipes. Copper causes blue/green stains on plumbing fixtures. It will also extend the life of the softener resin. Calculations on the chemistry of the raw water are done which include levels of hardness, alkalinity, pH, T.D.S and iron levels to determine if a pH neutralizer is needed or not. pH Neutralizer tanks have a control head and a backwash cycle, but for different purposes than a softener. A standard sized pH Neutralizer tank contains 120 lbs of food grade calcite. The lower pH water will slowly dissolve the calcite and raise the pH to near neutral. The weekly backwash is designed to agitate the calcite and prevent channeling thus keeping the water in maximum contact with all the calcite media. The backwash from this tank has just elevated calcium levels so it can be discharged into the septic tank, the town drain or a drywell.
Call us for a free appointment to evaluate your water issues, and recommend the correct equipment to remedy the problem. Water test kits are on our trucks or can be mailed to your home without delay. Call 508.272.6636
ADDING SALT TO BRINE TANK
Each regen cycle will deplete the salt in the brine tank by 8 to 12 lbs. The amount varies according to size of softener and other parameters. It is best to allow the salt level to lower itself over the course of 2 to 4 months or longer. Remove the cover and check the level. Its best to keep the salt level around 50% full for smaller families and 75% full for larger families. Brine can be made with as little as 2 bags in the tank. It is important to check for, and break up any hollow ” salt domes ” or ” salt bridges ” hidden under the visible salt level near the bottom of the tank. Just take a broomstick and break up the salt while the salt level is low. Salt bridges cause weak brine solution. If the softener is allowed to run out of salt, the only issue is that it will no longer soften the water. Unless unplugged, the control will continue to initiate regens without harm to the softener but water will be wasted every cycle.
 SOFTENER MAINTENANCE AND LIFETIME
SOFTENER MAINTENANCE AND LIFETIME
Modern water softeners require very little maintenance. These newer designs allow quick access to moving parts, o rings etc. Control heads should be checked over every year and broken down for cleaning every 2 to 3 years. It is important to have a good 5 micron high flow sediment filter in front of the softener to help keep maintenance at a minimum. Most well built softeners will last 15 years and beyond.
